Evaporation plant for the treatment of landfill leachate
The Evaporation Plant treats the retentate produced by a reverse osmosis plant to reduce the amount of concentrate to be sent for final disposal.
THE CLIENT.
- Gea S.r.l.– Greenthesis Group: Landfill in S.Urbano, Padua (IT) for municipal and/or special non-hazardous waste
- Treatment capacity: 3000 m³/g
- Technology used: Evaporation.
The thermal energy required for the process is provided with hot water supplied by the generator fed with biogas produced from the landfill. Vapor condensation is achieved by recirculating water in an adiabatic air condenser (dry cooler) for its cooling
THE PROBLEM.
The S.Urbano landfill produces about 280 t/day of leachate characterized by high concentrations of COD, ammonia, heavy metals, PFAS and chlorides The leachate is first treated with a reverse osmosis plant, which produces about 210 t/d of permeate with characteristics suitable for discharge to surface water and 70 t/d of retentate that is sent to the evaporation plant with a dry matter concentration of about 3/5%. The amount of distillate produced is about 60 t/d, while the final amount of concentrate at about 20 dry matter is 12 t/d The distillate is recirculated to the head of the osmosis plant.
THE GOALS.
- The evaporation plant must be able to treat leachate from other landfills operated by the Greenthesis group having different characteristics from that produced by the S.Urbano landfill
- The hourly quantities of distillate and concentrate produced can vary maximum within 5% of the design value
- Use of biogas produced from the landfill as an energy source for the evaporation process
- Process study in order to reduce chemical reagent consumption and heat exchanger flushing frequency
- High concentration yield
- Full automation of the process with the possibility of taking advantage of reliefs from the Industry 4.0 plan
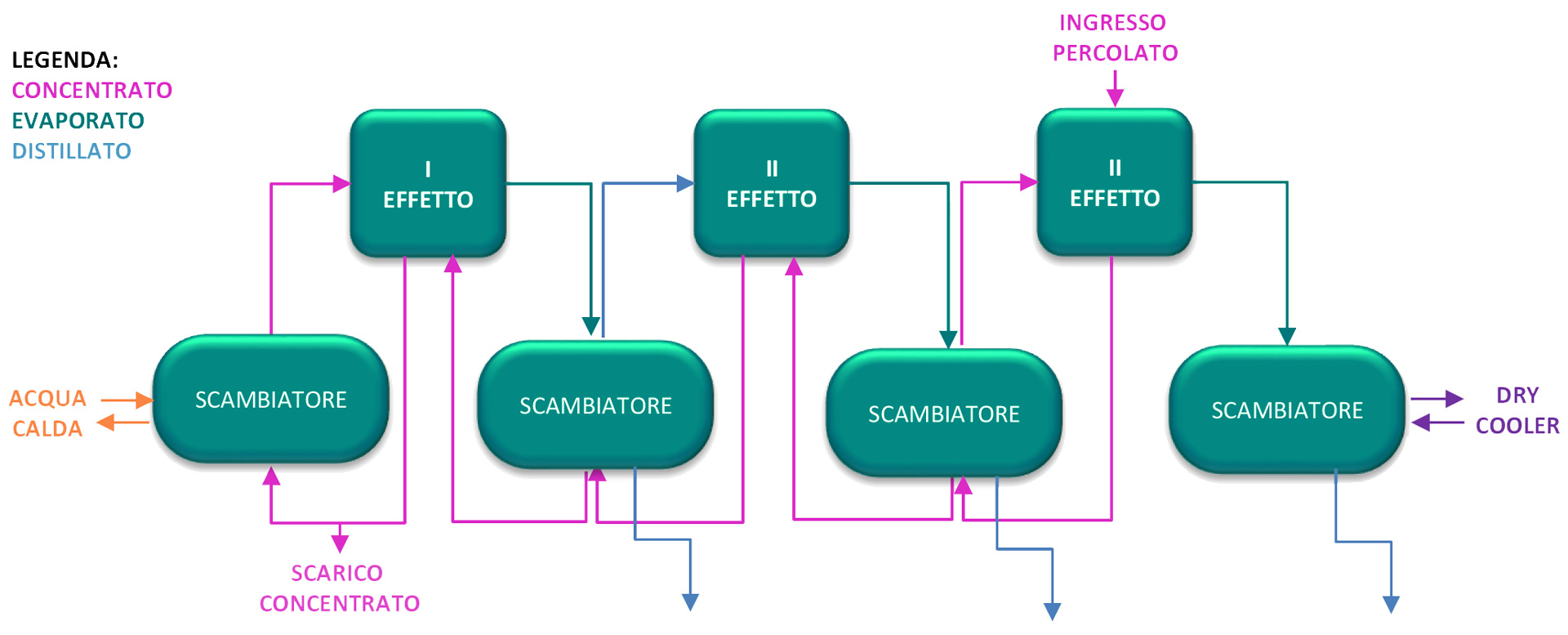
THE PLANT.
The evaporation system consists of three effects operating in countercurrent. Heat is supplied to the first effect
working at the highest evaporation temperature, while leachate feeding is done in the third effect
working at the lowest evaporation temperature and therefore with a higher degree of vacuum.
The vapors exiting the three effects are condensed in the heat exchangers.
The final distillate is sent to the head of the osmosis plant.
Given the high final concentration of chlorides, all parts in contact with the effluent are made of steel
SUPERDUPLEX to ensure corrosion resistance.
THE BENEFITS.
- High flexibility: leachates with varying chemical and physical characteristics can be treated;
- High reduction in final concentrate to be disposed of (about 85%), resulting in lower disposal costs;
- Ease of management, as the system is controlled continuously by PLC with the possibility of control and management via PLC networking;
- Optimization of electricity and chemical consumption
|
The Results
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
Input
|
Osmosis concentrate*
|
3000 kg/h
|
|
Output
|
Evaporation concentrate
|
500 kg/h
|
|
Distillate
|
2500 kg/h
|
|







