Nitrogen Removal and Recovery Plant
In recent years, great progress has been done in the construction of anaerobic digestion plants for biogas (or biomethane) production. In addition to the production of gas, with the fermentation process we obtaine as the final residue as well the digestate, which, thanks to the high concentration of ammonia nitrogen present in it, is highly appreciated as the fertilizer.
However, precisely because of the high concentration of ammoniacal nitrogen present in digestate, its direct spreading in the fields for the fertigation of farm crops generates negative consequences:
- The bad smells formation;
- The nitrogen oxides (N₂O) emission;
- The percolation through the soil of nitrates as final products of nitrogen oxidation.
In case the anaerobic digestion plant is located in agricultural areas where the nitrogen’s excess there is already present, there is also the problem of the digestate’s transport cost to the place of its spreading. As transportation costs continue to rise, it is inevitable the need to treat the digestate in in order to obtain it in more concentrated possible or solid form.
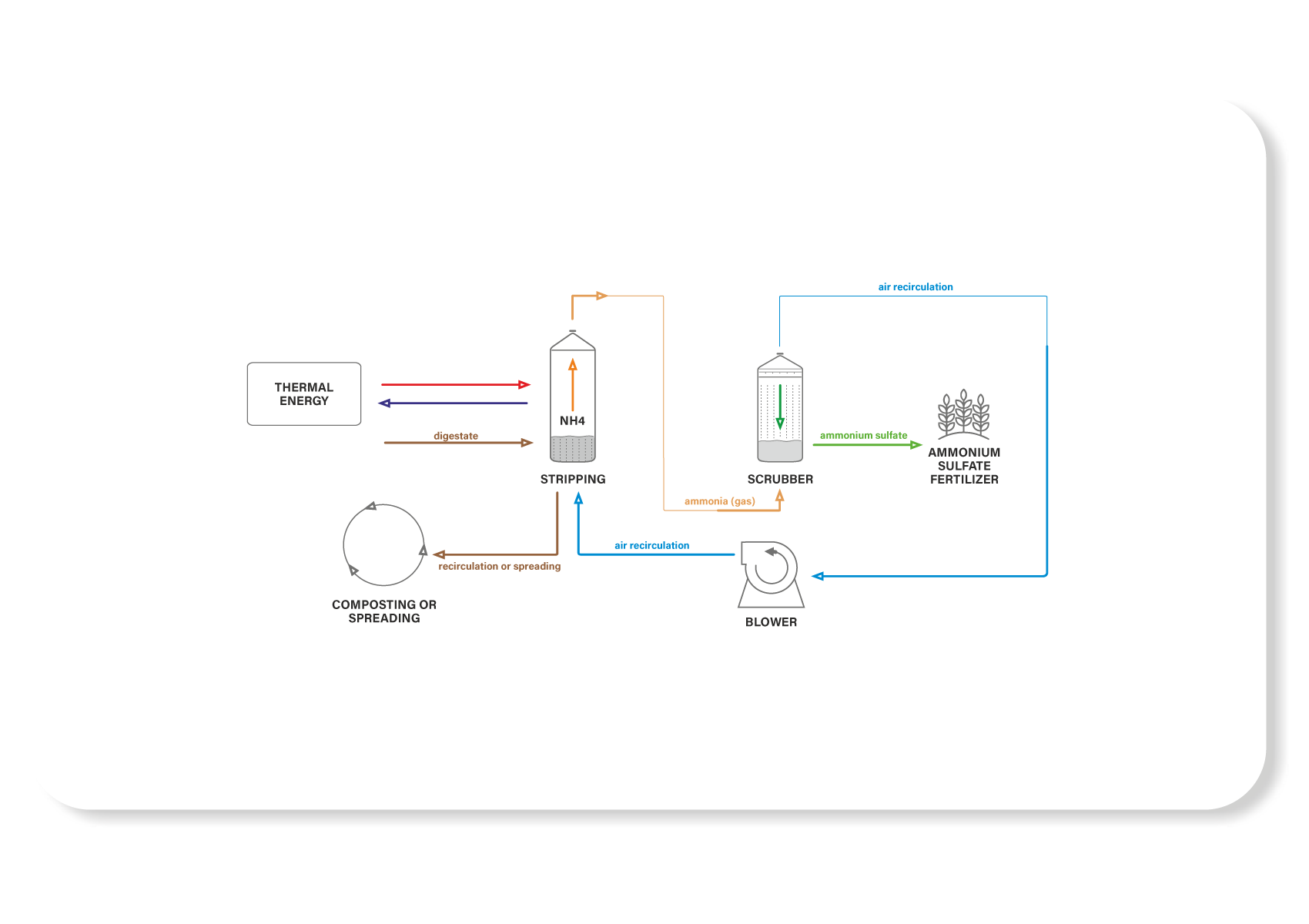
The hot stripping and recovery as ammonium sulphate is a valid alternative, compered to others more expensive and complicated treatments, to remove and recover the nitrogen. Since the demand for thermal energy is the limiting factor for high-temperature stripping, its application cannot be separated from the low-cost energy source availability, such as the one deriving from the cogenerators cooling water.
With the removal and recovery of the most part of nitrogen initially present in the digestate, it’s possible to obtain the following advantages:
- The separated liquid’s recycling at the head of the plant to dilute the biomass;
- With the same quality / quantity of inlet matrices, the surface required for digestate’s spillage is reduced (Italian law);
- With the same spreading surface, it is possible to increase the quality / quantity of the infeed matrices.
Plant diagram
No occlusions risk.
For the stripping section are used reactors where there are no air-liquid contact surfaces, as occurs in plant's usual towers with filling bodies that clog up quickly due to the high concentration of suspended solids and alkalinity present in the digestate;
The management simplicity.
The plant can be managed by unskilled personnel thanks to the simple and complete PLC-controlled process automation;
Limited use of chemical reagents.
To favor the ammonia's stripping is not necessary to add caustic soda to correct the digestate's pH;
The thermal energy recovery.
The required for the process thermal energy is recovered from the hot water produced by the cogenerators cooling;
Construction's speed
The plant is designed to ensure minimum assembly times;